
In a MySQL database, the where clause is used to filter the data according to the specified conditions. Using the where clause, you can retrieve, remove, or update a specific set of data in a MySQL database.
MySQL WHERE Clause in Python:
The WHERE clause has already been employed in one of our earlier tutorials:
- MySQL data update using Python
- MySQL data can be deleted using Python.
Use the WHERE clause in the SELECT statement to select data from a table based on a specific condition.
- Rows from the result set are typically filtered using the WHERE clause.
- Data from the MySQL Table can be retrieved, updated, and deleted with its assistance.
Syntax:
Following is the syntax of the WHERE clause −
SELECT column1, column2, columnN
FROM table_name
WHERE [condition]Example: Consider the following database named college and have a table name as a student.
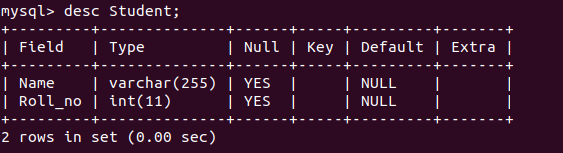
Schema of the database:
import mysql.connector
#Establishing connection
conn = mysql.connector.connect(
user='your_username',
host='localhost', password='your_password',
database='College')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
mycursor = conn.cursor();
# SQL Query
sql = "select * from Student where Roll_no >= 21;"
# Executing query
mycursor.execute(sql)
myresult = mycursor.fetchall()
for x in myresult:
print(x)
# Closing the connection
conn.close()
The where clause retrieves the records with roll number value greater than 21.
Note: also read about Drop Table Query – MySQL
Follow Me
Please follow me to read my latest post on programming and technology if you like my post.
https://www.instagram.com/coderz.py/
https://www.facebook.com/coderz.py
Staying up to the mark is what defines me. Hi all! I’m Rabecca Fatima a keen learner, great enthusiast, ready to take new challenges as stepping stones towards flying colors.
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.